What will we cover
Here's the architecture of what you will build at the end of this journey
TODO: Heres the video demo of how it will look when running end to end:
Stages
🧱 Launchpad – fundamentals
- Learn what Docker is, why it exists, and how it solves the problem of environment consistency.
- Understand containers conceptually and how they differ from virtual machines.
- Write Dockerfiles and build container images using best practices and layering principles.
- Use Docker Compose to run and wire together multiple containers locally.
- Learn YAML syntax and structure as the foundation for Kubernetes configuration files.
🔥Ignition 🔥 – first k8s cluster and pod**
- Launch a local Kubernetes cluster using kind and understand what components are created.
- Use core kubectl commands to inspect, apply, modify, and delete Kubernetes resources.
- Understand the difference between imperative and declarative resource management in Kubernetes.
- Get a high-level overview of Kubernetes cluster architecture, with concepts that will be revisited in depth later.
- Launch your first Pod and understand the structure and fields of a Pod manifest YAML.
- Learn why Pods are fragile and why higher-level workload abstractions are required.
Stage 1 : 🚀 Liftoff – launch all workloads on cluster with configuration
- Organize workloads using namespaces and understand logical isolation within a cluster.
- Deploy applications using ReplicaSets and Deployments and understand their reconciliation behavior.
- Launch and manage multiple deployments simultaneously on the cluster.
- Access running workloads using port forwarding for local testing and debugging.
- Run one-time and scheduled tasks using Jobs and CronJobs.
- Externalize configuration using ConfigMaps and understand when to use them.
- Manage sensitive data securely using Kubernetes Secrets.
- Design multi-container Pods using init containers and sidecars to support application behavior.
Stage 2 :🧭 Guidance, Navigation & Control – Networking
- Understand Kubernetes DNS and how service discovery works inside the cluster.
- Learn how Pods communicate with each other and what networking guarantees Kubernetes requires.
- Expose applications using Services and understand ClusterIP, NodePort, and LoadBalancer types.
- Control network traffic using NetworkPolicies to enforce isolation and security.
- Route external traffic into the cluster using Ingress resources using traefik.
- Understand the role of kube-proxy and how CNI plugins implement pod networking.
- Use the Gateway API as a modern, extensible alternative to traditional Ingress.
Stage 3 : 💾 Mission Data Systems – Persistent Storage
- Use ephemeral storage options like emptyDir and hostPath and understand their limitations.
- Learn what Persistent Volumes are and how storage is abstracted in Kubernetes.
- Understand reclaim policies and how Kubernetes handles storage after workloads are deleted.
- Request storage using Persistent Volume Claims and see how binding works.
- Use StorageClasses to define dynamic provisioning behavior for storage.
- Expose Pod and node metadata to applications using the Downward API.
- Run stateful applications using StatefulSets and understand their guarantees.
Stage 4 : 🎛️ Flight Control Systems – Controls in place
- Configure liveness, readiness, and startup probes to control workload health.
- Define resource requests and limits to manage CPU and memory consumption.
- Understand Quality of Service (QoS) classes and how Kubernetes prioritizes Pods under pressure.
- Control scheduling behavior using Pod Priority and Preemption.
- Enforce fair usage and prevent resource exhaustion using resource quotas.
Stage 5 : 📦 Mission Payload Integration – Packaging and Deployment
- Package and template Kubernetes manifests using Helm charts.
- Customize Kubernetes configurations using Kustomize overlays and patches.
- Build CI/CD pipelines to test and deploy applications automatically using GitHub Actions.
- Using testContainers to do integration testing.
- Implement GitOps workflows using Argo CD to manage deployments declaratively.
Stage 6 : 📡 Mission Operations (Houston) – Monitoring and Observability
- Revisit probes from an operational perspective to understand real-world failure signals.
- Use DaemonSets to deploy monitoring and system agents on every node.
- Debug running Pods using ephemeral containers without restarting workloads.
- Explore the cluster visually using the Headlamp dashboard.
- Collect and query metrics using Prometheus.
- Visualize metrics and build dashboards using Grafana.
- Centralize logs using Loki and correlate them with metrics.
- Trace requests across services using OpenTelemetry.
- Systematically troubleshoot failing applications and Pods using observability data.
Stage 7 : 🛰️ Orbital Maneuvering – Scaling
- Automatically scale workloads using Horizontal Pod Autoscaler (HPA).
- Control where Pods run using taints and tolerations.
- Influence scheduling decisions using node affinity rules.
- Control Pod co-location and separation using pod affinity and anti-affinity.
Stage 8 : 🔐 Command Module Hardening – Security
- Implement fine-grained access control using Role-Based Access Control (RBAC).
- Secure Pods using security contexts to restrict privileges.
- Use hardened container images to minimize the attack surface using docker hardened images.
- Authenticate workloads using Service Accounts.
- Store and manage secrets securely using Vault as an external key store.
- Manage encrypted secrets using Sealed Secrets and External Secrets Operator.
- Enforce baseline security standards using Pod Security Admission.
- Manage TLS certificates automatically using cert-manager.
- Integrate Kubernetes authentication with OIDC using Keycloak.
- Control and mutate resources using admission controllers.
- Enforce policy-as-code using OPA or Kyverno.
- Scan source code and container images using TruffleHog and Trivy.
Stage 9 : 🌕 Lunar Orbit Operations – Deploy to Cloud
- Deploy Kubernetes clusters on EKS, GKE, and AKS using Terraform.
- Scale cluster nodes dynamically using Cluster Autoscaler or Karpenter.
- Load test applications using k6 to validate performance.
- Distribute workloads evenly using topology spread constraints.
- Perform safe Kubernetes cluster upgrades.
- Protect availability during disruptions using Pod Disruption Budgets.
- Maintain cluster health through routine operational tasks.
- Design and operate a truly highly available Kubernetes cluster.
Stage 10 : 🧪 Mission Extensions
- Hook into Pod and container lifecycle events using lifecycle hooks.
- Implement a service mesh using Linkerd for traffic management and security.
- Perform progressive deployments using Argo Rollouts.
- Build a full DevSecOps pipeline integrating security into delivery.
- Implement backup and restore strategies using Velero and Rook.
- Introduce controlled failures using Chaos Mesh to test resilience.
- Monitor systems using eBPF-based tooling such as Coroot.
Stage 11 : 🚀 Towards Mars
- Design and implement custom CRDs and Kubernetes operators.
- Extend the Kubernetes API server with custom functionality.
- Build a homelab using k3s and expose services securely via Cloudflare Tunnel or Tailscale.
- Implement event-driven autoscaling using KEDA.
- Manage application behavior dynamically using feature flags.
- Build internal developer platforms using Backstage.
- Analyze and optimize cluster costs using Goldilocks and Kubecost.
- Use Kubernetes as a control plane for external infrastructure with Crossplane.
- Harden clusters using CIS benchmarks and runtime security tools like Falco.
- Manage clusters declaratively using Cluster API.
- Design and operate multi-cloud Kubernetes architectures.
- Build serverless workloads using Knative.
- Prevent misconfigurations using Datree.
- Learn how to engage with the Kubernetes community through SIGs and TAGs.
Prerequisites
- This course assumes that you come with bare basic knowledge about linux.
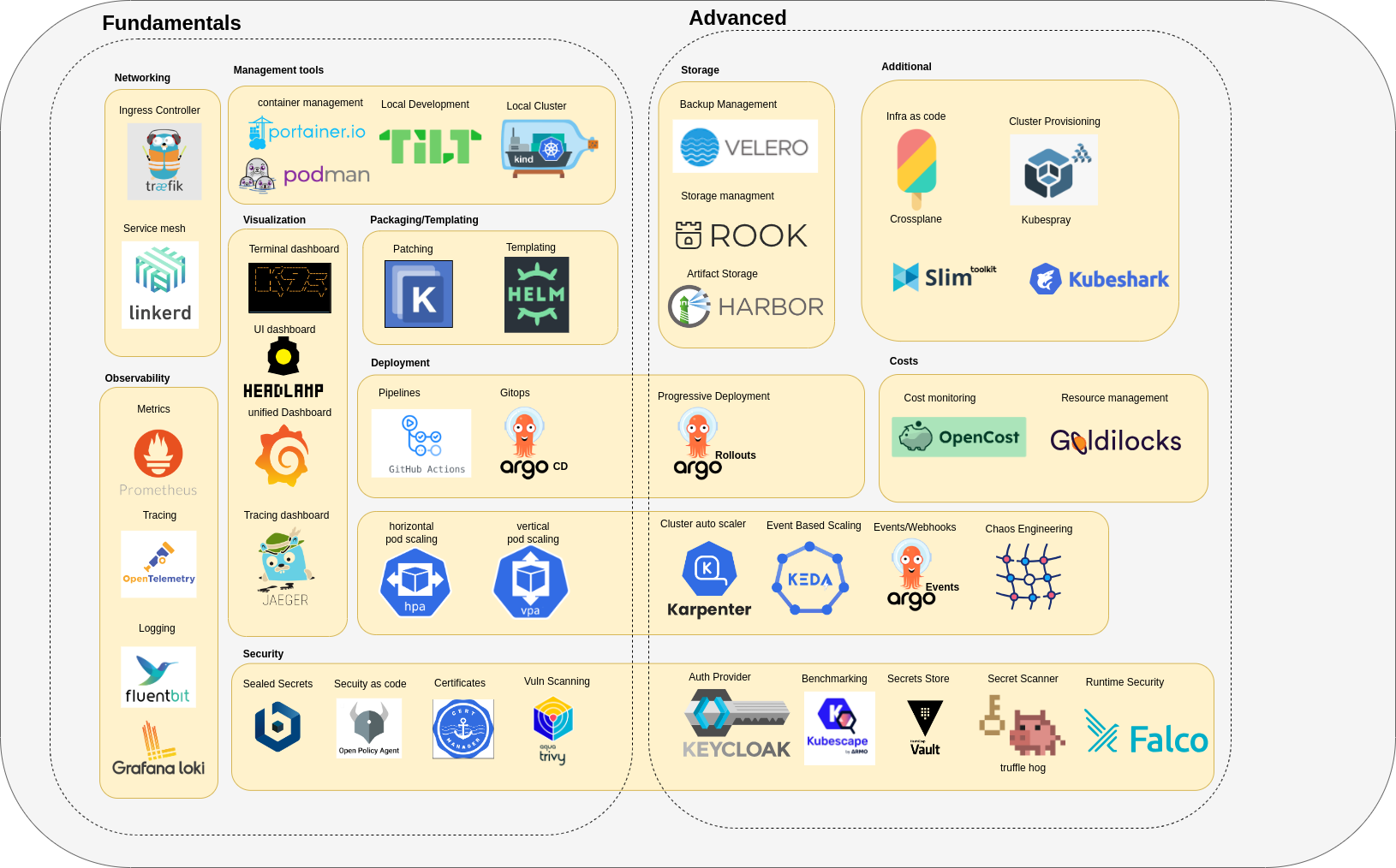
Tools
| Category | Tools |
|---|---|
| Backend API | Golang,Python |
| Sql Database | Postgres,Mysql |
| Nosql Database | MongoDB |
| Local Development | Tilt |
| Dashboard | Headlamp,k9s |
| Container Management | Docker, Podman |
| CI | Github Actions |
| GitOps | ArgoCD |
| Progressive Deployment | Argo Events, Argo Rollouts |
| Secret Store | Vault |
| Ingress Controller | Apisix |
| Packaging | Helm |
| Patching | Kustomize |
| Logging | Fluentd (agent), Loki (backend) |
| Service Mesh | Istio |
| Monitoring | Prometheus, Grafana |
| Compliance Monitoring | kubebench |
| Policy Engine | OPA/Kyverno |
| Policy Checker | Kubescape |
| Backup and Restore | Velero |
| Load Testing | hey,Kube-monkey |
| Cluster Provisioning | Kubespray (optional) |
| Serverless | OpenFaas |
| Container Builds | Buildah |
Extra:
- https://github.com/groundcover-com/caretta
- Dapr
- Dagger